Table Of Contents
What Is Business Operations?
Business operations can be defined as daily activities or deliverable business to sustain themselves, enhance the enterprise's value, and derive income from it. The employees perform these operations.
Sustainability depends on the type of employees hired by the organization and the kind of technology utilized to deliver business results. The business operations focus on the day-to-day activities performed in the business. Such activities help the business to earn profit or revenues or cover the cost of operations.
Key Takeaways
- Business operations are daily activities or deliverable businesses to survive, improve the enterprise's value, and obtain income. The employees handle the business operations.
- The various business industries are retail, service, manufacturing, and technology.
- The business operations ensure that all resources and assets are fully used to get the business results and objectives.
- Moreover, they must coordinate well among departments, namely accounting, finance, marketing, and sales.
- The elements of the business operations are process, location, technology, business machinery & equipment, and staffing.
- Moreover, the business activities help the business to gain profit or revenues or make up the operations expenses.
Business Operations Explained
A business operations plan refers to the process or carrying out an entity's daily procedures through proper coordination between different departments to manufacture, market the goods and services, and earn revenue and profit.
Different parts of the business perform different operations which help it to run smoothly and achieve its aim. The employees, management, directors, laborers, etc all are an integral part of managing business operations.
The goods and services offered may be tangible or intangible, but every business tries their best to reach out to the maximum market possible to cater to the needs of consumers.
Types
The various types of business operations plan are given below:
#1 - Production
This is the main aim of setting up of an organization. Every organization produces some type of goods or services for the benefit of the community by selling which, they can earn revenue and cover the cost.
#2 - Marketing
Marketing is an integral part of the business because it helps in earning revenue and expand and grow. Marketing helps in informing the consumers about the products and services manufactured in the business so as to earn revenue and profit.
#3 – Finance
This is the part of the business that helps in managing the financial resources, and channelizing them towards optimum use. This operation helps the entity to use the money earned by properly investing in useful areas that will earn return that can be further invested from expansion.
#4 - Human resource
This operation refers to the employees, management, laborers, etc, whoever help in running the day to day operations smoothly by contributing their time and effort.
Functions
Let us look at the different business operations functions.
- The primary function is to help a business earn income, as sustainable operations could only achieve this.
- The business has to ensure that all resources and assets are utilized to their fullest to drive the business results and objectives. Wastage of resource is a loss for the business.
- They have to ensure that there is an establishment of good coordination among different departments, namely accounting, finance, marketing, and sales.
- True and correct strategy will help in aligning the mission with the procedure so as to achieve the aim with least cost and maximum revenue.
Examples
Some examples of business operations functions are given below:
The Service industry would have different sets of business operations compared with the manufacturing and retail industry. The Merchandising industry has a model that believes in selling merchandise inventory quickly. Therefore, these types purely depend on the industry level it works.
The business varies with different industries and can be classified as follows: –
#1 - Retail Industry
The retail industry deals with products that could be immediately sold to customers at a price that matches their paying capacity. The business operating in such inventory needs to have a robust inventory management system. The system should be so robust that the business should differentiate between a finished product or a product in low demand with high demand.
#2 - Service Industry
The service industry can be bifurcated based on the nature of business operations. They can be classified as back-end and front-end. The front-end business works with the customers and tries to meet their expectations. To meet customer expectations, they have to develop mechanisms that record the feedback given by the customer that allows them to prioritize their requirements and deliver optimized business outcomes.
The backend business operations strategy should work towards supporting the front-end part of the business. They should help the front-end people with forecasts and projections that prevent the business from exceeding their budgeted or expected costs.
#3 - Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturing businesses focus on transforming raw materials into marketable finished products. To produce quality finished goods, they have to access quality raw materials from the suppliers. Additionally, they have to focus on eliminating any potential bottlenecks that may arise in the manufacturing of products and then shipping them to the correct business outlet or warehouse.
#4 - Technology Industry
To have a high-impact business, the technology business operating in the industry has to hire the right skill set required to execute the job function or project it has in hand. To meet the business requirement, such hires may be trained first on utilizing tools and skillset to accomplish the job at hand.
Elements
Managing business operations tend to be different and distinct as per the business types, size, and industry. Online stores or E-store operations are different from brick and mortar stores. Therefore, it is necessary to chalk out the broad elements.
The elements are primarily composed of the following elements: –
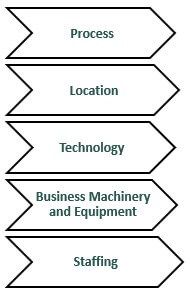
#1 - Process
The process is termed as the backbone of the business operations. It has a lasting impact on efficiency and productivity. The processes can be performed both on a manual basis and with the application of automated software. The activities that form the part of the process should be documented carefully and should be named as the standard operating procedure.
Such standard operating procedures could then allow quality managers to go through such documents and, in time, drive continuous improvements.
#2 - Location
For running a business smoothly, it is critical to shortlist a favorable business location. If the business is large corporate, it should easily be accessible to its employees. If the business is small and led by a solo entrepreneur, he can work from remote locations or rent virtual offices to drive value generation.
#3 - Technology
A business operations strategy cannot sustain itself if it does not adopt the latest technology. Fruitful leverage of technology in the business drives operational excellence and sustainability.
#4 - Business Machinery and Equipment
This aspect focuses on the hardware utilized by the business to run its business operations. The business should invest in the right machinery and equipment to sustain its operations.
#5 - Staffing
Any business to meet its organizational needs and business targets must possess the right talent in place. The right talent should have the desired skill set and domain expertise to drive operational excellence, thereby ensuring the sustainability of the business operations. The staffing needs of the organization vary with size and process needs.
A small process or organization may have limited staffing needs and a closed group of employees. A larger organization may have unlimited staffing needs to meet its business objectives.
How To Improve?
- Measurement of Key Performance Indicators or Performance: - The business should establish the right metrics and measures that help measure the milestones that are to be achieved by the business. It should establish the right goals and targets that could be met easily.
- Analyze and Understand the Trends Dominating the Industry and Markets: - To stay competitive in the industry, a business has to stay updated with the trends in the industry. The business should have the ability to learn from the trending topics and innovate from them to deliver projects that exceed the expectations of their customers or clients.
- Streamlining the Deliverables and Projects in Pipeline or Process: - The business should eliminate redundant and non-value-add activities and attempt to streamline the process so that the business achieves the right business outcomes.
Benefits
- It helps in streamlining of operation process in a smooth and structured way which will help to achieve the ultimate objective. .
- It leads to effective utilization of assets and resources of the business. If resources are not used properly, then it leads to wastage and loss for the entity. The assets do not grow and the business easily loses its place in the highly competitive market.
- It offers the opportunity to replicate innovations achieved in one process to be replicated in the process with similar objectives. This is very important because each department in a business is interlinked. Innovation in one department and not in the others will not help the business to grow or expand. If growth is the aim them the management should concentrate on all parts equally and bring innovation or implement new technology in all areas.
- It helps in identifying lagging areas and make plan to either revamp them or eliminate them. These are the areas that are perhaps not generating enough revenue or dragging the company towards losses. A good business operation will identify these areas.
Limitations
- Creation of departments within a business which might be unnecessary or lead to resource wastage.
- There might be lack of coordination among team members. This may create a hindrance in the smooth performance of business operation.
- At times, the balance between the execution and business strategy may not be aligned with one another. This may lead to disastrous consequences since the company is not actually working towards achieving the purpose but working in a mismanaged way due to which the directors and management is not clear about the correct path or using incorrect strategy, leading to effort wastage.
